Leave Your Message
Choosing an Energy Efficient Heat Pump for your home is a crucial decision that can significantly impact your energy consumption and environmental footprint. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, heat pumps can provide up to 300% efficiency, meaning they can generate three times more energy in heating than they consume in electricity. This remarkable efficiency not only translates into lower energy bills but also contributes to reduced greenhouse gas emissions, making them a sustainable choice for homeowners looking to enhance their energy efficiency.
Industry expert Dr. Emily Johnson, a leading researcher in the field of HVAC technologies, emphasizes the importance of selecting the right heat pump: "Investing in an Energy Efficient Heat Pump is not just about comfort; it's about creating a sustainable future. Homeowners can realize significant energy savings while supporting environmentally friendly practices." As we navigate the myriad of options available on the market, understanding the key factors that contribute to a heat pump’s efficiency is essential for making an informed choice. By carefully evaluating these parameters, homeowners can ensure they select a system that meets their heating and cooling needs while maximizing energy efficiency.

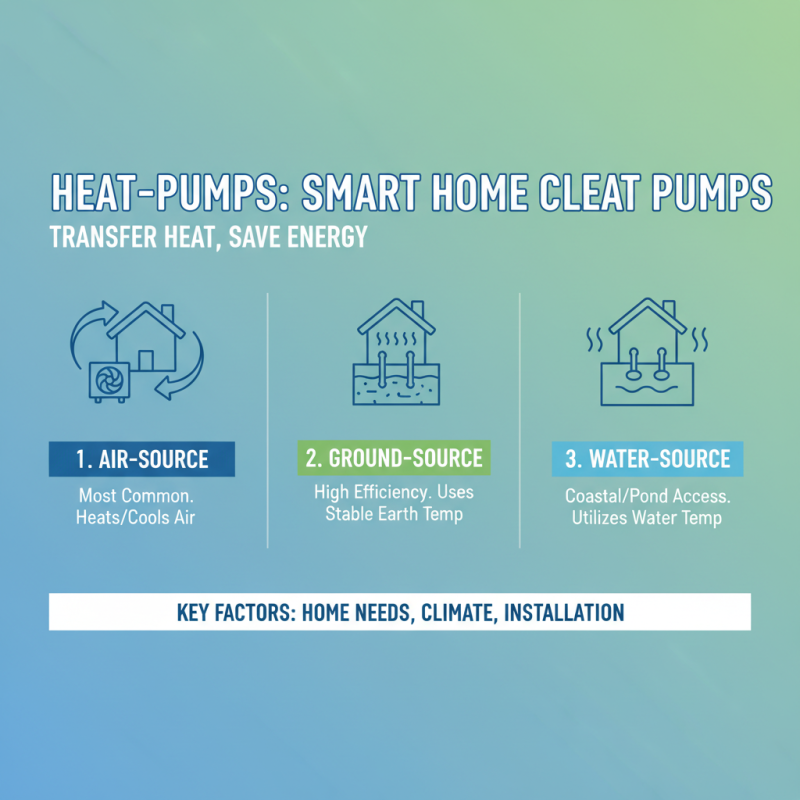
Heat pumps are vital components of energy-efficient heating and cooling systems for homes. They operate by transferring heat rather than generating it, which allows them to utilize energy more effectively. There are several types of heat pumps, each with distinct characteristics and efficiency ratings that can significantly impact their performance. The most common types include air-source, ground-source (geothermal), and water-source heat pumps. Selecting the right type depends on your home's specific needs, the local climate, and the installation conditions.
Efficiency ratings are crucial when evaluating heat pumps. The Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) and the Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF) are key metrics that reflect a heat pump's cooling and heating efficiency, respectively. Higher ratings indicate more energy-efficient systems, which can lead to lower utility bills and reduced environmental impact. It is essential to compare these ratings among different models and to consider the heat pump's performance in real-world conditions, as efficiency can vary based on factors like installation quality and home insulation. By understanding these types and their efficiency ratings, homeowners can make informed decisions that contribute to energy conservation and cost savings.
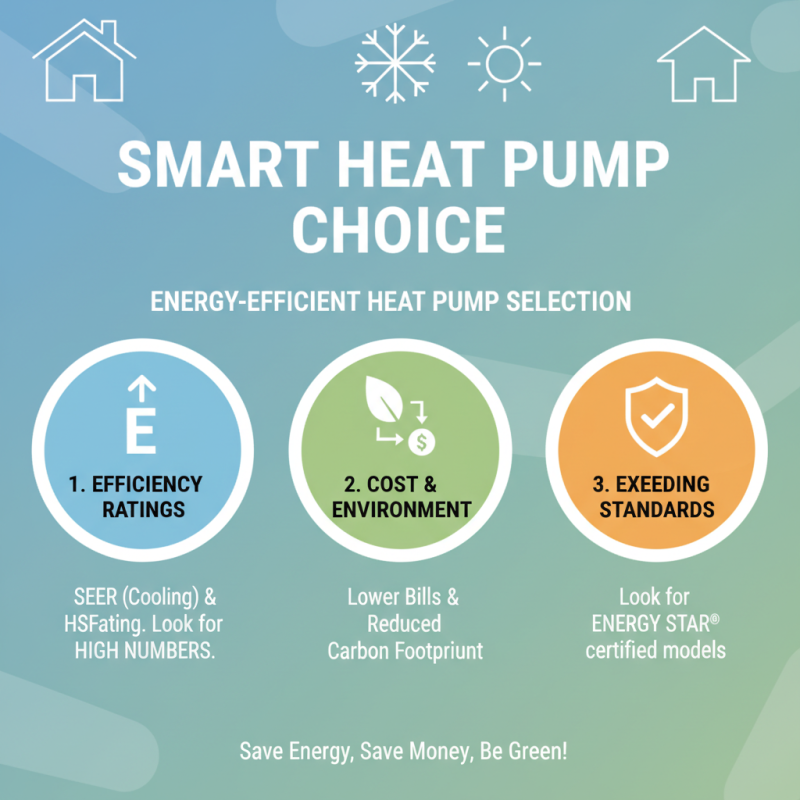
When selecting an energy-efficient heat pump for your home, several key factors play a crucial role in ensuring you make the right choice. First and foremost, consider the heat pump's efficiency ratings, typically represented by the Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) for cooling and the Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF) for heating. Higher ratings indicate better energy efficiency, which translates to lower operational costs and a reduced environmental impact. It is advisable to look for models that not only meet but exceed the minimum efficiency standards outlined by energy regulations.
Another important factor to assess is the size of the heat pump relative to your home. An improperly sized unit can lead to inefficiencies, as an undersized pump may struggle to maintain comfort levels, while an oversized one can cycle on and off too frequently, wasting energy and causing unnecessary wear and tear. Additionally, consider the specific climate of your region, as some systems perform better in certain temperature ranges. Lastly, evaluate the noise level of the heat pump, especially if you plan to install it near living spaces; quieter units enhance comfort without disrupting the peace of your home. By carefully weighing these considerations, you can choose a heat pump that not only meets your heating and cooling needs but also aligns with your commitment to energy efficiency.
When selecting an energy-efficient heat pump for your home, evaluating the size and capacity requirements is crucial for optimal performance and comfort. The right heat pump should be capable of efficiently heating and cooling your space without overworking or underperforming. To begin, you'll need to assess the square footage of the areas to be conditioned, taking into account any open spaces, ceiling heights, and architectural features that might impact air flow and temperature regulation.
Additionally, consider the climate in your region. Heat pumps are rated by their heating and cooling capacity, usually measured in British thermal units (BTUs). For instance, a unit that is too small will struggle to maintain comfortable temperatures during extreme weather, while an overly large unit can lead to short cycling, where the pump frequently turns on and off, reducing efficiency and lifespan. Performing a Manual J calculation or consulting with a professional can provide a precise estimation of the required capacity, ensuring that your heat pump meets both your home’s demands and energy efficiency goals effectively.
When considering the budgeting for the purchase and installation of a heat pump system, it is crucial to first understand the range of costs associated with these systems. According to a report from the U.S. Department of Energy, the average price of a heat pump can vary significantly depending on the type and capacity, generally ranging from $3,500 to $7,500. Additionally, installation costs can add anywhere from $1,000 to $3,000 to your total expenditure, making it essential to factor in both the unit's purchase price and the installation expenses when planning your budget.
Moreover, it’s important to analyze potential long-term savings that energy-efficient heat pumps can provide. The American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy (ACEEE) estimates that homeowners can save up to 50% on heating and cooling costs compared to traditional HVAC systems. These savings should be considered as they may offset the initial financial outlay over time. Additionally, many local utilities and government programs offer rebates and tax incentives for energy-efficient upgrades, which can further alleviate the financial burden. Therefore, structuring your budget not only to account for upfront costs but also potential savings and financial incentives can lead to a more informed and economical decision in the long term.
This bar chart illustrates the Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER) of different types of heat pumps, helping homeowners to compare and choose the most efficient option for their needs.
Maintaining the efficiency of your heat pump is crucial for maximizing performance and reducing energy costs. Regular maintenance is key. Start by checking and replacing filters monthly, as dirty filters can obstruct airflow and strain the system. Ensuring that the outdoor unit is clear of debris, such as leaves and dirt, is also vital. This allows the heat pump to function optimally without additional strain that could lead to failures.
Another tip is to schedule professional inspections annually. A technician can identify potential issues that might not be apparent during regular maintenance. They can clean the components, check refrigerant levels, and ensure the system is operating within the manufacturer’s specifications. Moreover, consider insulating your ducts if they are in unconditioned spaces, as this minimizes energy loss and enhances efficiency.
Lastly, adjusting your thermostat settings can lead to significant efficiency improvements. Utilize programmable or smart thermostats to manage heating and cooling schedules effectively. By automatically adjusting the temperature during hours when the house is unoccupied, you'll save energy without sacrificing comfort. Implementing these tips will not only enhance the efficiency of your heat pump but also prolong its lifespan, ensuring a comfortable home for years to come.
| Feature | Importance | Tips for Maintenance | Efficiency Enhancements |
|---|---|---|---|
| SEER Rating | Higher ratings indicate better efficiency | Regularly clean or replace air filters | Install a programmable thermostat |
| HSPF Rating | Measures heating efficiency | Check ducts for leaks | Use zoning systems |
| Size | Proper sizing ensures effective heating and cooling | Schedule annual professional inspections | Upgrade insulation in your home |
| Noise Level | Quieter models improve comfort | Ensure outdoor units are clear of debris | Consider sound blankets for outdoor units |
| Refrigerant Type | Newer models use eco-friendly refrigerants | Monitor for refrigerant leaks | Opt for variable speed compressors |